
Here's a special treat for all my visual learners! Check out these infographics I created to DDx between all the Gram positive Cocci...
Laboratory workup of Gram POS Cocci
Staphylococcus species
Streptococcus species
1. Determine the morphology/grouping of the gram-pos organism
GRAM POSITIVE COCCI IN...
CHAINS

SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Streptococcus
-
S. pneumonoiae
-
Viridans streptococci (S. mutans)
-
S. pyogenes
-
S. agalactiae
-
Enterococcus faecalis
-
Peptostreptococcus
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
CLUSTERS

SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Staphylococcus
-
S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus
-
Gram pos cocci in CLUSTERS
2. Perform a Catalase Test
Catalase: an enzyme that catalyzes the release of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)



CATALASE NEGATIVE:
No bubbles are formed
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Streptococcus
-
S. pneumonoiae, Viridans streptococci (S. mutans), S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, Enterococcus faecalis, Peptostreptococcus
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEG


CATALASE POSITIVE:
Bubbles are formed
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Staphylococcus
-
S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus
-
Gram pos cocci in CLUSTERS
-
Catalase POS
Staphylococcus Species Workup
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
If catalase is POSITIVE, then perform a Coagulase Test


COAGULASE NEGATIVE:
No clot formed on slide (left) or tube (right) tests
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
S. epidermidis
or
S. saprophyticus
-
S. epidermidis vs. S. saprophyticus
-
Gram pos cocci in clusters
-
Catalase POSITIVE
-
Coagulase NEGATIVE


COAGULASE POSITIVE:
Clots/clumps formed on slide (left) or tube (right) tests
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
S. aureus
-
S. aureus
-
Gram pos cocci in clusters
-
Catalase POSITIVE
-
Coagulase POSITIVE
If Coagulase Test is NEGATIVE, determine Novobiocin sensitivity

NOVOBIOCIN RESISTANT
NOVOBIOCIN SESNSITIVE
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
S. saprophyticus
-
S. saprophyticus
-
Gram pos cocci in clusters
-
Catalase POSITIVE
-
Coagulase NEGATIVE
-
Novobiocin RESISTANT
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
S. epidermidis
-
S. epidermidis
-
Gram pos cocci in clusters
-
Catalase POSITIVE
-
Coagulase NEGATIVE
-
Novobiocin SENSITIVE
Perform a Clindamycin Induction Test (D Test)
-
What you need to know:
-
Since clindamycin and streptogramin are among the few drugs of choice in the treatment of methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infections, knowing the resistance to these antibiotics is imperative.
-
The D test is used to study the macrolide lincosamide streptogramin resistance (MLSB), both constitutive and inducible as well as macrolide streptogramin resistance (MSB) in Staphylococcus aureus.
-
Basically, the D test is performed to determine if S. aureus is susceptible to Clindamycin.
-
-
How testing is performed:
-
Erythromycin (macrolide) and clindamycin (lincosamide derivative) discs are placed adjacent to each other over the Mueller Hinton agar medium inoculated with the test organism.
-
The test is performed in the same MHA plate in which the antibiotic sensitivity test is being done, taking into consideration that the discs are placed adjacent to each other maintaining the distance.
-
Clindamycin resistance can be induced by Erythromycin which causes the Kirby Bauer zone around the Clindamycin disc to be blunted and form a "D" if clindamycin can be induced by erythromycin to be resistant. So this is called INDUCABLE RESISTANCE.
-


D
-
Interpretation:
-
The organism susceptible to clindamycin without any flattening of the zone (D test negative) near clindamycin disc (resistant) = Macrolide streptogramin resistance (MSB)
-
Susceptible to both antibiotics = No resistance
-
Flattening of the clindamycin zone (D test positive) near the erythromycin disc (resistant) = Inducible MLSB (IMLSB)
-
The growth of the organism up to the edges of the disc = Constitutive MLSB (CMLSB) Resistance
-
Streptococcus Species Workup
S. pneumonoiae (encapsulated)
Viridans streptococci (S. mutans)
S. pyogenes (Group A Strep)
S. agalactiae (Group B Strep)
Enterococcus faecalis (Group D Strep)
Peptostreptococcus (Anaerobe)
If catalase is NEGATIVE, then determine the pattern of hemolysis on sheep blood agar, then continue the appropriate testing algorithm to determine the bacterial organism.
Some bacteria produce extoxins that cause the lysis of RBCs which can be seen on a blood agar plate
GAMMA HEMOLYSIS
ALPHA HEMOLYSIS
BETA HEMOLYSIS

Partial clearing
Green color
Degrades hemoglobin into biliverdin
Complete clearing
Yellow color
Produces hemolysins
No clearing
White/transparent color
Negative for hemolysins
Quellung test
Bacitracin sensitivity
Aerobe vs. Anaerobe

Optochin sensitivty
Tests for presence of a capsule
"Quellung= SWELLING"
NEGATIVE
No swelling
No capsule
POSITIVE
Swelling around capsule
Encapsulated

RESISTANT
No clearing
SENSITIVE
Clearing around disk
BILE SOLUBLE
Clearing of broth in presence of bile
NOT SOLUBLE
Turbid solution
No lysis present
Bile Solubility testing

Some bugs make a self-lysing enzyme to depress the growth of old colonies. The presence of bile salt will accelerate this .
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Viridans Strep
S. mutans &
S. mitis
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
ALPHA (partial) hemolysis
-
NEG Quellung rxn
-
NO capsule
-
-
NOT bile soluble
-
Optochin RESISTANT
S. pneumo
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
ALPHA (partial) hemolysis
-
POS Quellung rxn
-
ENCAPSULATED
-
-
BILE SOLUBLE
-
Optochin SENSITIVE
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Group A Strep:
S. pyogenes
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
BETA (complete) hemolysis
-
BACITRACIN SENSITIVE
Group B Strep:
S. agalactiae
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
BETA (complete) hemolysis
-
BACITRACIN RESISTANT
SENSITIVE
Clearing around disk
RESISTANT
No clearing


AEROBE
Growth near top of tube
(highest O2 concentration)
Grows in 6.5% NaCl
ANAEROBE
Growth at base of tube
(lowest O2 concentration)
No growth in 6.5% NaCl
SCROLL OVER TO REVEAL
Answer
Enterococcus
Group D Strep
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
GAMMA (no) hemolysis
-
AEROBIC organism
-
Growth in 6.5% NaCl
Pepto-
streptococcus
S. bovis
-
Gram pos cocci in CHAINS
-
Catalase NEGATIVE
-
GAMMA (no) hemolysis
-
ANAEROBIC organism
-
No growth in 6.5% NaCl
SUMMARY
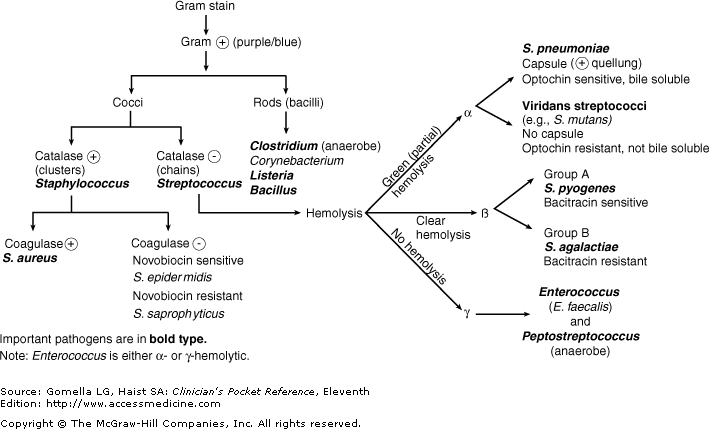
See below for how to differentiate between the various Streptococci bacteria
based on hemolytic patterns and other laboratory tests.


anaerobes

MICRO & IMMUNO
INDEX
PREVIOUS TOPIC
Gram pos vs. Gram neg classification
NEXT TOPIC-
Gram positive RODS

